The 4C's.
Every diamond, like a human fingerprint, has certain distinguishing characteristics. The 4Cs – color, clarity, cut and carat weight—are the globally accepted standards for assessing the quality of a diamond.
Clarity
Diamond clarity is a measure of the purity and rarity of the stone, graded by the visibility of these characteristics under 10-power magnification. A stone is graded as flawless if, under 10-power magnification, no inclusions (internal flaws) and no blemishes (external imperfections) are visible.
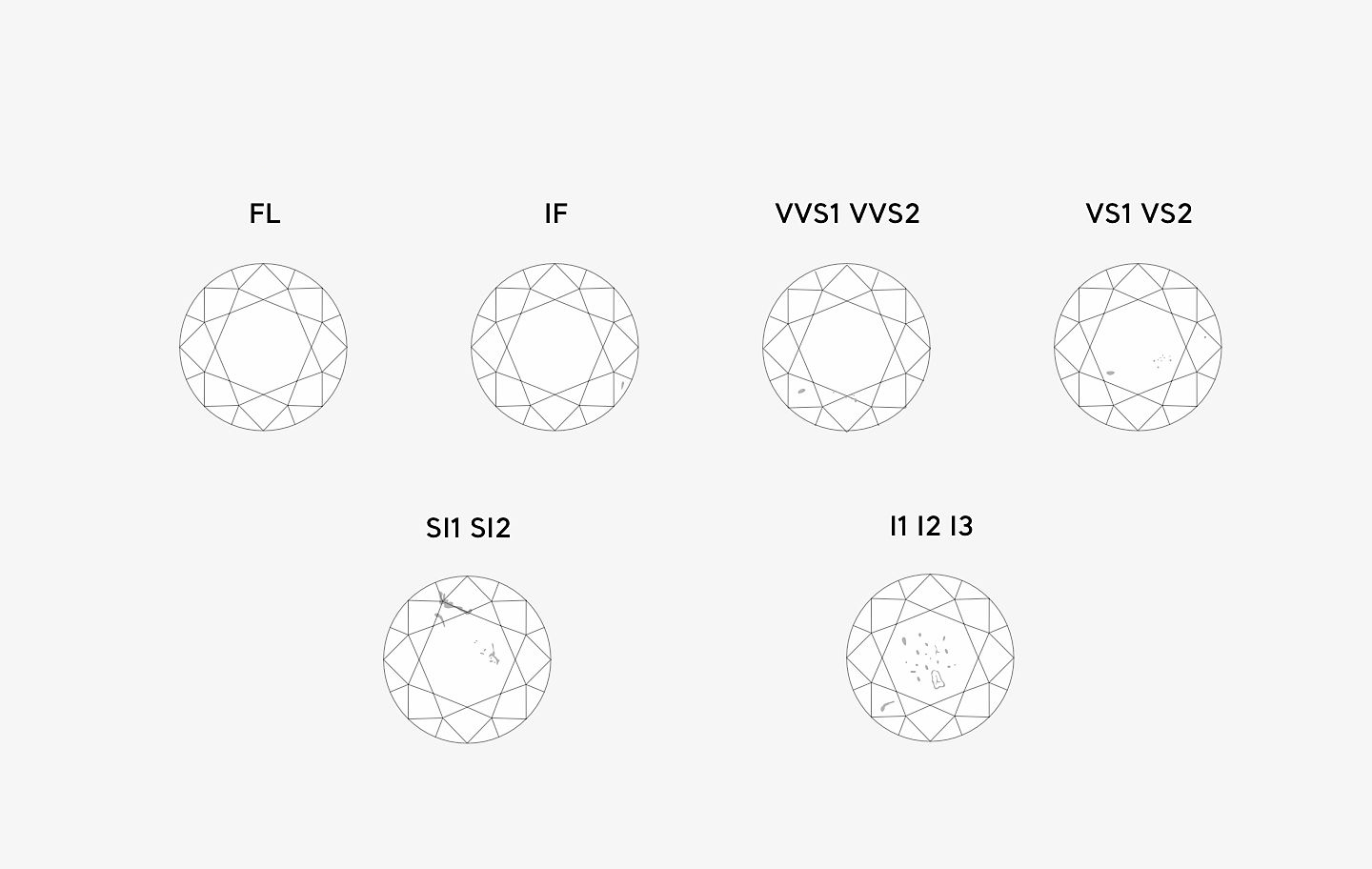
Diamond Clarity Chart
Diamond Clarity Chart
Diamond inclusions are internal flaws.
FL : Flawless
IF: Internally Flawless
VVS1 VVS2: Very, Very Slightly Included
VS1 VS2: Very Slightly Included
SI1 SI2: Slightly Included
I1 I2 I3: Imperfect
Diamond inclusions are internal flaws.
FL : Flawless
IF: Internally Flawless
VVS1 VVS2: Very, Very Slightly Included
VS1 VS2: Very Slightly Included
SI1 SI2: Slightly Included
I1 I2 I3: Imperfect
A diamond with a poor clarity grade has multiple inclusions, which directly affects sparkle. Because inclusions hinder the refraction and return of light, the lower the clarity grade, the cloudier the diamond will appear.
Color
Color refers to the natural tint inherent in white diamonds. In nature, most white diamonds have a slight tint of yellow. The closer to being “colorless” a diamond is, the rarer it is. The industry standard for grading color is to evaluate each stone against a master set and assign a letter grade from “D” (colorless) to “Z” (light yellow).
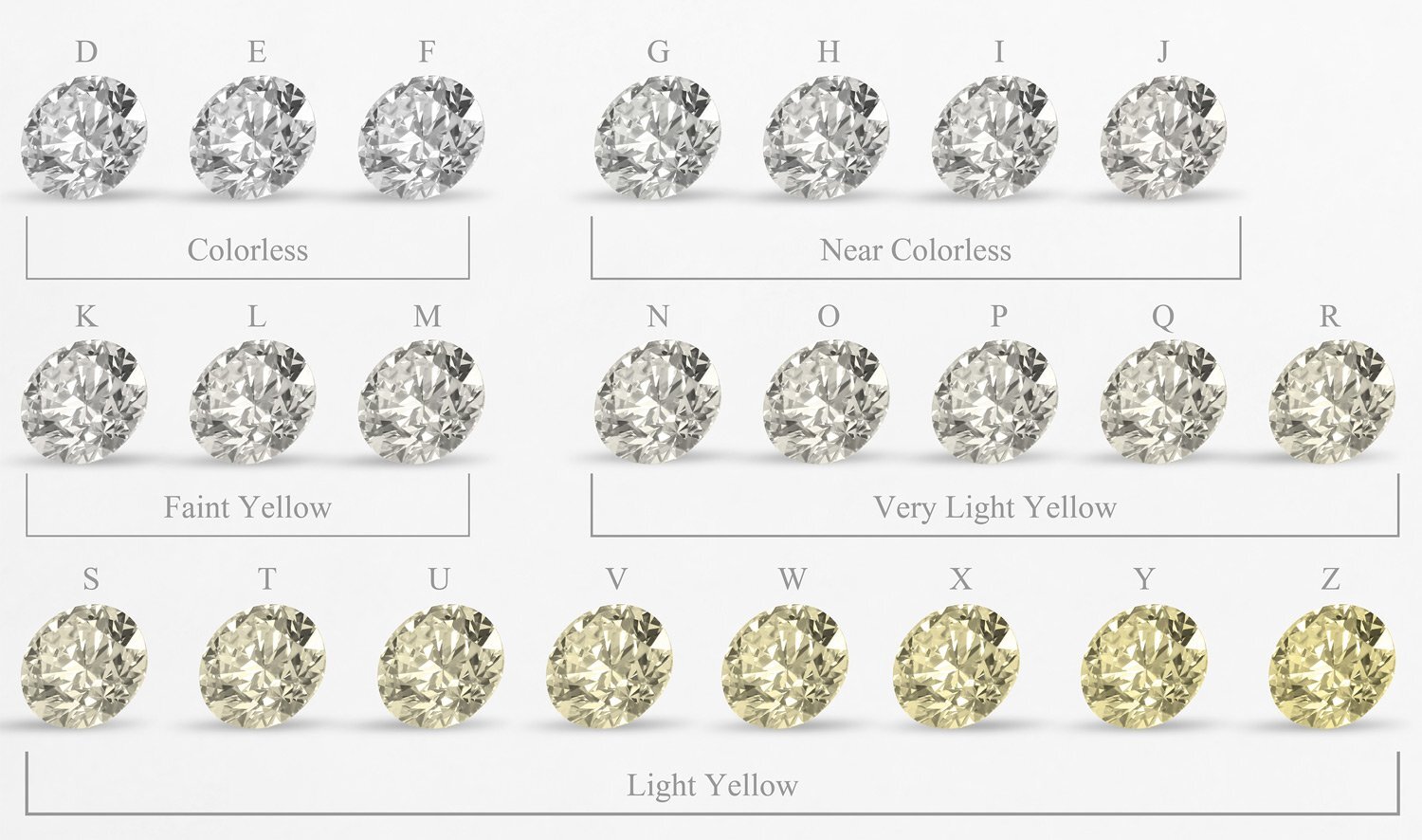
Color Grading Chart
Color Grading Chart
DEF: Colorless
GHIJ: Near Colorless
KLM: Faint Yellow
NOPQR: Very Light Yellow
STUVWXYZ: Light Yellow
DEF: Colorless
GHIJ: Near Colorless
KLM: Faint Yellow
NOPQR: Very Light Yellow
STUVWXYZ: Light Yellow
Color is the second most important of the 4Cs because the color grade directly affects the stone’s appearance. Diamonds with a poor color grade can appear slightly yellow instead of the desired brilliant white.

Cut
The most important of the 4Cs—cut—refers to how a diamond’s facets interact with light. It is determined by symmetry, proportion and polish. More than any other factor, cut determines the beauty of the stone. If a diamond is cut poorly, it will appear dull even if it has a high color and clarity grade. If a diamond is cut well, it will reflect and refract light for maximum brightness and sparkle.
Cut grades are: “excellent,” “very good,” “good,” “fair” and “poor”.
Cut grades are: “excellent,” “very good,” “good,” “fair” and “poor”.
Carat
Carat weight can appear differently across different diamond shapes such as round brilliant, princess, pear, oval, cushion, marquise, emerald, radiant or heart. A diamond may have a higher carat weight without appearing larger and two diamonds of the same carat weight can vary in size if one is cut deeper than the other. In other words, it is important to note that carat weight does not necessarily denote size. One carat equals to 0.2gr.
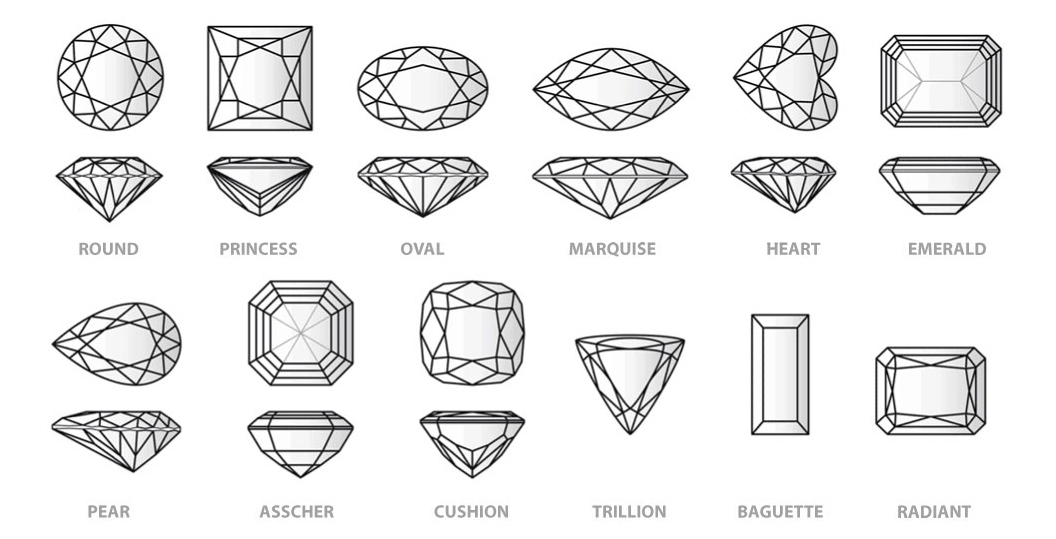
Shape and Cut
Diamond shape refers to the geometric appearance of a diamond. Diamond shapes are categorized into two groups: round diamonds and fancy shape diamonds. Round diamonds, also known as round brilliant cuts, are the most traditional diamond shape. Fancy shape diamonds refer to any diamond that is not a round brilliant.It’s important to note that diamond cut and diamond shape are not the same thing.
A diamond’s cut determines how its facets interact with light. A shape describes the geometric appearance of a diamond. Cut defines what the shape of a rough diamond will be not the other way around.
A diamond’s cut determines how its facets interact with light. A shape describes the geometric appearance of a diamond. Cut defines what the shape of a rough diamond will be not the other way around.
Solitaire types
Classic: the most popular type of solitaire, simple and all-time-classic.
Flame: curved, giving a modern touch and bringing more volume to the ring.
Rosette: one diamond in the middle and others circling it like the petals of the rose.
Trilogy: three diamonds
Illusion: A cluster of small diamonds appearing as one, giving a nice impressive result at low cost.
Pavé : the surface appears to be paved with diamonds set closely together.
Flame: curved, giving a modern touch and bringing more volume to the ring.
Rosette: one diamond in the middle and others circling it like the petals of the rose.
Trilogy: three diamonds
Illusion: A cluster of small diamonds appearing as one, giving a nice impressive result at low cost.
Pavé : the surface appears to be paved with diamonds set closely together.


Certification
All our diamonds are certified by gemologists or gemological institutes as IGI or GIA.
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact us,
Syrivelis Konstantinos, GIA GG Gemologist.
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact us,
Syrivelis Konstantinos, GIA GG Gemologist.